
JIOrings, a real asset
The importance of approvals
Day after day the O-rings have to meet more and more requirements in matters of environment and security. By the same token, public organizations impose more and more rigorous and restrictive requirements on materials or compounds that form the seals which are aimed to get in contact with water, gas, food products, chemistry products…
In JIOrings we are really committed to preserve the quality and security of the compounds that form our seals. In order to increase the value of our products, gain competitive advantage and develop a reliable brand, we are immersed in a continuous certification process that comprises the following points:
· Our own approvals: In this case we have different compounds with our own homologation as well as some others which are undergoing the process to be homologized.
· Our main suppliers’ approvals: As distributors we require of our suppliers all the certifications our clients need.
· In addition, in JIOrings, being distributors, we meet the standards of REACH regulation as well as the standards of RoHS directive.
Our own approvals
In some cases, when some compounds have been really successful (for instance, those compounds in stock offered in different measures or compounds which have been highly demanded by our clients), we decided to take a step forward and homologate the mixture (such as the food-grade silicone JA7006F-134662) on our own. That way we can provide our clients with a verified and warranted quality level according to the results obtained in the testing carried out by an independent laboratory. In these cases, the achievement of the homologation, as stated by the standards of the American agency FDA (Foods and Drugs Administration), implies that the technical file should have the original certification of the homologation.
In some other cases, we feel indebted to homologate a specific mixture due to the market’s demands. When we started the new stage of internationalization for our silicone plugs for wine barrels we soon realized that, beyond the quality of the pieces, we also had to pay attention to all the documentation related to the quality of the mixture we were about to provide to our buyers. In the first stage, we managed to get the FDA homologation, but as in some cases it turned out not to be enough, we got on to work. Thanks to the inestimable collaboration of Intertek, we achieved the BfR (Bundesinstitut für Risikobewertung – The German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment) certification, which meets the requirements of the European Union’s 1935/2004 regulation and it allows us to export our plugs all around the world, and with all the guarantees.
Homologation process
In general, laboratories require rubber samples that are called slabs. They are semi-finished pieces, in a standardized size that allow carry out some tests which are defined by the most common international regulations (ASTM, DIN, ISO, etc…). The aforementioned tests are executed under really strict conditions and they will be only homologated in case the results are within the established limits.
So far we have certified all the approvals on our own with the help of two close companies: the Technological Centre of La Rioja and the Intertek’s branch in Bilbao. However, we would not discard, in case it would be necessary, the help of a foreign laboratory for specific approvals, such as that of the drinking water.
And now, what?
We firmly believe that quality is an added value that JIOrings offer in each sale. We constantly work to ensure that our seals meet all quality, health, security, environment and social responsibility standards in nearly all markets. In addition, we are aware our clients appreciate the efforts we are making in the last years.
We inform you we have already updated the “Official Approvals” section in our web. You could find there a table where we indicate all the approvals by compounds. In case it is a specific mixture we homologated, you can download it automatically. In the other cases, however, we indicate the adequacy of the approvals for each mixture. This table contains information that we will be updating just as we get more approvals, be our own approvals, be approvals certified by our suppliers.
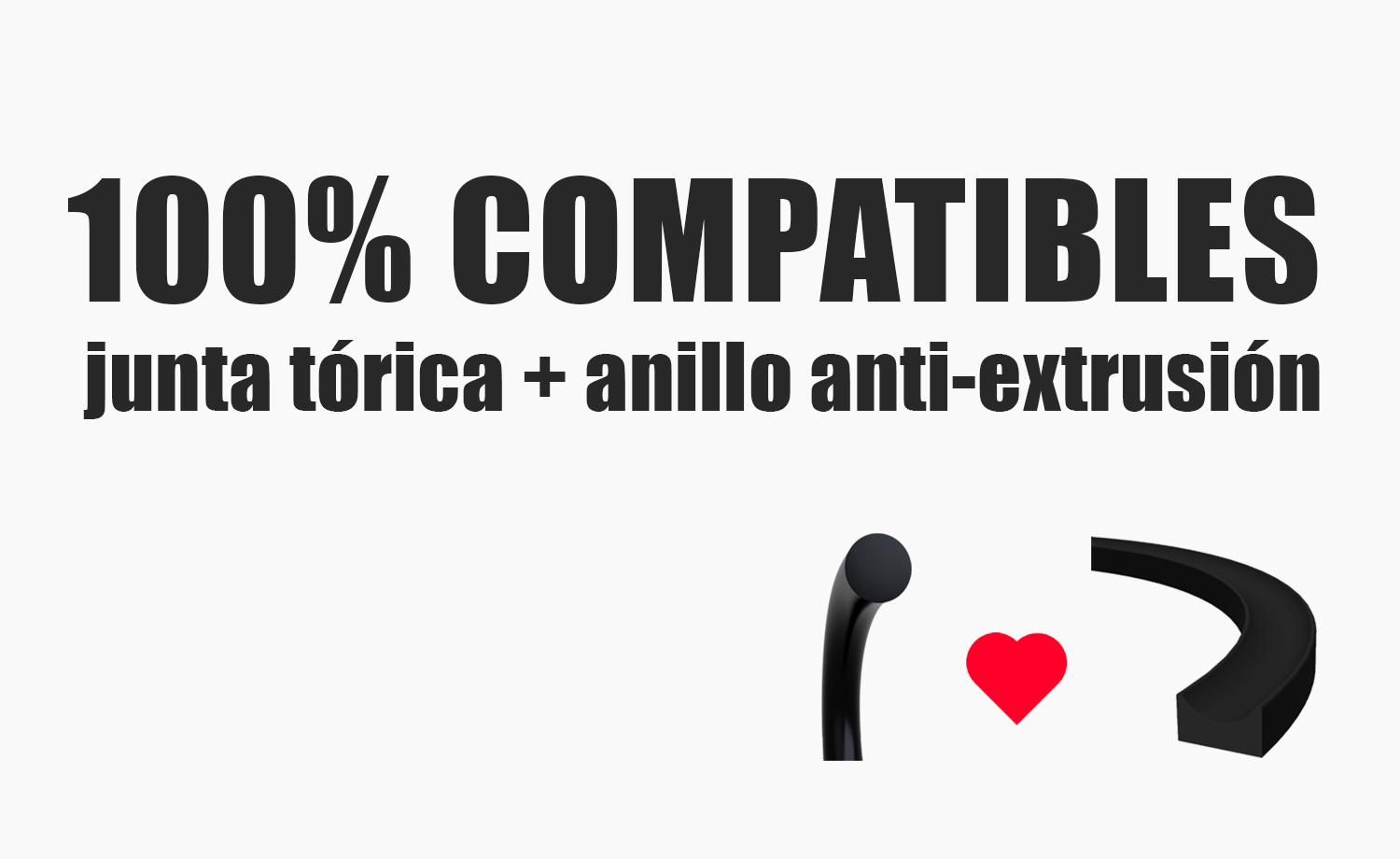
The back-up rings (BUR) and the O-Rings, the perfect tandem
Back-up rings + O-Rings = 100% compatible
Some time ago we spoke about the O-Rings and how good they were when a risk of extrusion from the housing could exist. The O-Rings create the seal effect pressing against the housing parts that hold it, but the capacity of the ensemble depends basically on these three factors: (1) the correct choice of the O-ring, (2) the surface finishing of the housing and (3) the play between the elements.
When the O-Rings are called to exercise the seal in circuits in which the pressure reaches high levels, one of the risks to be considered is that of the ring extrusion from the housing. Such a risk is increased when the O-Ring compound is soft.
In order to avoid this risk we may rely on back-up rings (BUR), also known as anti-extrusion rings. The back-up rings are designed to guarantee a high level of seal performance in contact with the O-Ring. Otherwise said, they aim to protect the O-ring so that it may develop its task.
The choice of the right back-up ring lies in the following points which should be born in mind:
• The compounds chosen for the back-up rings must meet all of the compatibility requests of the fluids requested of the O-Rings.
• The hardness to support the other pressure loads must be suitable.
• The resistance to the usage and ageing must be high, to guarantee good performance for the entire life of the O-ring to which they are required to protect.
• The measure of the back-up ring, of course, must go with the O-ring that protects.
If the choice is the correct one the back-up ring will provide an excellent performance, as a back-up element for the piston and shank seals that may be generally found in hydraulic static circuits and hydraulic dynamic circuits. The back-up ring could be located in the rear or under the pressure of the sealing element which is holding, although there could also be different housings that hold two back-up rings, each from a different side of the O-ring.
At JIOrings we have NBR90 back-up rings according to the Parker® Standard:
From: -006 to -460 (ø3,56mm to 394,31mm).
Thickness: 1,14/1,24 1,14/1,35 1,02/1,27 1,52/1,93 2,44/2,97.
* Under request, we may provide different measures and other materials.
If you want to purchase them in our online store you can find them by product (BUR or Back-Up Ring) and size. You can also take the British Standard number that the O-ring has as a reference (for example, BS211) to search in the “Description”.
| Type | Profile | Material | Pressure [Bars] |
Temperature [ºC] |
Check stock in real time |
| Back-up rings |  |
NBR | ≤400 | -20º to +100º |

The wrong election of a seal could have terrible consequences
If there is any gas, choose RGD, ED Resistant or AED seals
The O-ring, the most universal seal, is the most used seal in fluid-tights because of its excellent effectiveness-cost relationship. Simple as it may be, it can also be manufactured in many different materials and it has a wide range of uses. When it comes to choose the most suitable material, the fluid to be tightened and the temperature are elements of paramount importance to make the good choice. By the same taken, History has shown us that no failure must be allowed.
NASA’s Challenger Space Shuttle could be one of the most well-known and tragic cases, when it broke apart 73 seconds into its flight due to the wrong choice of an O-ring. The seals used in the shuttle were FKM seals, and they were not designed to fly under unusually cold conditions as in this launch, so the seals lost their elasticity. As a result, seals lost their capacity to return to their original shape after the foreseen movement and this led to the disaster.
Nowadays, more and more clients ask us for O-rings for different fields (such as pharmaceutical, aeronautic, chemist, biomedicine, drinking water, food, gas industry…) and applications with high standards. Indeed, we just want to highlight in this post the consequences of the gas that may result in because of a wrong choice, as high pressure applications need the right seal for being efficient.
The term RDG (Rapid Gas Decompression), also known as ED (Explosive Decompression), is one of the main causes for tight failures when using seals, especially in many high pressure processes. It is a phenomenon that occurs when a pressurized gas reaches the outside very quickly and makes rubber seals from the equipment fail.
To avoid this risk, at JIOrings we offer RGD, ED Resistant or AED (Anti-Explosive Decompression) O-rings which are specifically manufactured to prevent this failure from happening and endure the quick gas decompression. The most commonly used material for RGD certified O-rings is Viton® or FFKM®, but they can also be manufactured with different materials, such as HNBR, Aflas® or FFKM.
